Any animal in the jungle or even in captivity has to eat to survive. They prey on other animals
for food. Mostly a predator’s prey is something smaller than its size, but some small predators eat bigger prey too. In the case of frogs, they are fed mostly on snails, insects, worms, small fish, and spiders while bigger frogs go for bigger prey.
Still, the majority of frog species eat insects. In eating, frogs swallow the whole food since they have no teeth that would grind and cut the food into pieces. Instead, they make use of their eyes to swallow the food. They do this by sinking their eyes through the skull’s opening in order for the food to be forced down the throat.
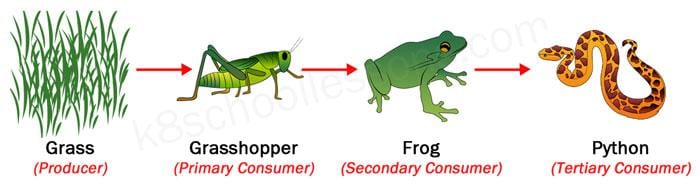
On the other hand, frogs become food for other animals. This is the rule of the food chain. Unfortunately, they are found at the bottom. Despite having defense mechanisms and escaping strategies, there are frogs who don’t survive and serve as a meal for other animals.
In the freshwater, frogs play an important role. Each frog undergoes a process of transformation. In each stage, the frog’s life is vulnerable to predators. In the rainforest, frogs are seen as tasty snacks to animals eating meat. In other words, there are many predators ready to attack and eat them.
What is Predation?
Predation entails action and a relationship between two creatures. Predators are animals that hunt, catches, and eat other animals. They could keep their prey dead or alive before they are eaten. This always leads to the death of the prey, and the prey ends up being eaten. These predators can be carnivores and omnivores. Some examples of predators include cats, snakes, crocodiles, sharks, whales, and more. Some animals are predators and scavengers. Meanwhile, the animals hunted and eaten are called prey.
Both the prey and predator go through evolution. They prey is always a big part of the predator’s environment. The predator dies without food. Whether they like it or not, predators must undergo important changes just to eat the prey. These are having good speed, camouflage, sense of sight and smell, stealth, hearing, immunity, and appropriate mouth part for digestion.
In the same way, prey has to make sure it will not be eaten. It has to improve its speed, poison, camouflage, sense of smell, hearing, and sight, and more. A type of predator is called the ambush predator. It just sits and waits. They catch their prey with strategy or stealth instead of strength or speed. These predators just quietly hide and strikes. They also camouflage and stay alone.
Non-fast moving predators use this method. It is more efficient, but hunting is more effective when the predator is faster than its prey. However, in long runs, stalking or ambushing is commonly used.
List of Frog Predators
1. Birds

Living in the fresh biomes gives a threat to frogs and tadpoles. They are surrounded by reptiles and birds. Birds living near freshwater survive on tadpoles and smaller frogs. Big bullfrogs may survive the smaller birds but not the Herons.
Herons eat aquatic animals like fish and frogs as they wade in pools, marshes, and swamps. They build their nests in trees and bushes near the body of water. their nests come in colonies. These birds stand with their neck bent like an ‘S shape.’ As they fly, their legs are trailing loosely while their heads are held back against their bodies. Their wings are broad, and their bills are pointed. There is a tiger, night and typical herons. Other birds include geese, swans, ducks, ravens, hawks, crows, and gulls.
Avian birds look down from above to look for food. They possess amazing eyesight then strikes the prey with precision and quickness. Unfortunately, frogs end up in their bellies. Some of the birds are hornbills, hawks, eagles, and owls. A hawk is a raptor. This group eats meat. Only meat. Not plants or vegetables. They then hunt for food. Their prey is mammals like rats, mice, squirrels, voles, and rabbits. Reptiles to are part of their diet, and sadly, even frogs are not exempted.
2. Snakes

They are at risk also for swimming snakes like water moccasins and garter snakes. Water snake’s foods are fish and amphibians, including frogs and toads. As this snake gets bigger, its food choice changes from fish to frogs. It swallows its food alive. While waiting in the shallow waters, they open their mouth widely for the prey to pass by; then, it snaps its jaws. They search on rivers, lakes, under the rocks, and more. This snake has venom like proteins found in their saliva. If the frog escapes, it can follow the frog with blood trains.
Snakes are fed on meat. They even eat their fellow. Some snake species are hunters, while others just ambush their prey. They are tricky and sneaky. Some will look like a worm, while others will keep themselves hidden in the sand. Most snakes live on lizards, frogs, fish, eggs, and more. When eating, they swallow the whole food. The food is wrapped and constricted slowly as their coils are tightened and the animal is squeezed to its last breath.
Although the prey is big, snakes have powerful muscles for moving and swallowing big prey. Taking the food down the throat takes 10 minutes to 1 hour. The food in their stomach is digested or broken up in days or even months. Some snakes just eat a couple of times in a year.
3. Variety of Mammals

Because frogs have secretions on their skin, some mammals don’t eat them. However, not all frogs taste bad for some predators. Majority of mammals in the freshwater prey on frogs. They are otters, minks, raccoons, and opossums. In addition, there are leopards, jaguars, and other large cats. Bats make frogs part of their diet as they go out of the night. They locate the frogs by their sounds.
4. Water Creatures
In order for frogs to breathe, they need to keep their skin wet, so they spend much time in the water. This brings them to the danger of facing predators. Fish and aquatic turtles are dangers to frogs. In addition, some other carnivorous frogs eat them too.
5. Smaller Predators
The eggs and tadpoles are tiny. They face the threat of being eaten by leeches, diving beetles, newts, dragonflies, or other bugs. Smaller tadpoles are mostly eaten.
Defense Mechanisms
Frogs have their way of defending themselves from threats in their environment. These are some ways by which they protect themselves.
1. Eggs and Larvae
Although larvae and eggs cannot protect themselves clearly, frogs have a strategic way to lay eggs, and that means a higher chance of surviving. Some frogs lay eggs in protected areas. Eggs are clustered within the zone, or eggs are in strings hoping that predators will not grab the whole eggs. The young ones don’t group so they will not be a target. They use their speed to run from predators.
2. Adult Colors
Camouflage is the most common way for frogs to hide. The skin color matches their typical habitat’s color. Frogs living in the water possess a lighter stomach and darker back while the tree frogs are green, blending with the leaves. Others make use of stripes. Frogs of bright colors warn their predators that they are poisonous and they must be avoided.
3. Adult Movement
To escape, frogs must jump. This leaping movement distracts the predator. This way, the predator cannot follow the frog’s scent.
4. Size
Size is an advantage for a frog. If a frog is small, it means it would be harder for predators to find it. Sometimes, being big is really an advantage if the predator is smaller than the frog.
5. Toxicity
Making sure no predator wants to eat you is indeed the best way. Some frogs get their toxicity from what they eat.
6. Vocalizations
Other frogs make a loud sound to scare the predator away.
In the animal world, particularly in the food chain, animals are meant to survive while others die. That is the rule of the jungle. The weakest die and the strongest wins. It is sad, but that’s how nature works. It just follows the rule of nature. Animals have no choice of what their roles are in the food chain. In this chain, the strong and wise animal eats the weak and helpless prey while the weak prey always finds their out to escape and hide from their predators.
Conclusion
Animals have their own way to protect themselves, and by chance, they either die or live if they are fortunate. To keep the ecosystem, this chain has to work. If the chain is destroyed, then problems will occur. In today’s society, it is a fact that humans are one of the major reasons why the natural ecosystem is destroyed. Animals lose their habitat because of man’s action in search of development and wealth. As a result, a lot of animals die, leading to extinction and endangerment of multiple animal species. This must be stopped.